지난 포스팅에 이어서 Geometry에 대해서 살펴보겠다.
이전 포스팅에서는 WireframeGeometry, BoxGeometry에 대해서 살펴봤는데 나머지 잘쓰이는 Geometry에 대해서 살펴보겠다.
마찬가지로 같은 코드에서 실습을 해보면서 익혀보겠다.
모든 예제 소스는 유튜브 GIS Developer 님의 강좌를 보면서 작성하였다.
공식문서를 보고, Three.js에서 각 Geometry의 생성자를 보고 각 Geometry객체에대해서 쉽게 알 수 있다.
직접 해보면서 값을 넣어보면서 변화를 보다보면 각 변수가 어떤 역할을 하는지 어렵지 않게 알 수 있을 것이다.
아래는 실습 javascript 코드이다.
import * as THREE from 'three'
import {OrbitControls} from 'OrbitControls'
class App{
constructor(){
const divContainer = document.querySelector("#webgl-container");
this._divContainer = divContainer; //다른 메서드에서 참조 할 수 있도록 함.
// [STEP 1] Renderer 세팅
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
// 생성할때 다양한 옵션을 설정할 수 있음.
antialias : true // antialias : true => 경계선의 계단현상을 없애줌
});
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePiexelRatio);
divContainer.appendChild(renderer.domElement); //canvas타입의 DOM 객체
this._renderer = renderer; // renderer를 다른 메서드에서 참조 할 수 있도록 정의
// [STEP 2] Scene 객체 생성
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
this._scene = scene; // scene을 다른 메서드에서 참조 할 수 있도록 정의
// [STEP 3] Camera 객체 생성
this._setupCamera();
// [STEP 4] Ligth 객체 생성
this._setupLight();
// [STEP 5] 3차원 모델 객체 생성
this._setupModel();
// 마우스 움직이는대로
this._setupControls();
window.onresize = this.resize.bind(this);
this.resize();
requestAnimationFrame(this.render.bind(this));
}
_setupCamera(){
const width = this._divContainer.clientWidth;
const height = this._divContainer.clientHeight;
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
width / height,
0.1,
100
);
camera.position.z = 2;
this._camera = camera;
}
_setupLight(){
const color = 0xffffff;
const intensity = 1
const light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(color, intensity);
light.position.set(-1, 2, 4);
this._scene.add(light);
}
_setupControls(){
new OrbitControls(this._camera, this._divContainer);
}
_setupModel(){
// ## BoxGeometry
// ## wireFrameGeometry
// const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1,1,1); //가로 세로 깊이
// const geometry = new THREE.CircleGeometry(0.8, 32, 0, Math.PI/2);
/*
# 1. CicleGeometry
constructor(
radius?: number, : 반지름 | default :1
segments?: number, : 원판의 분할갯수 | default : 8 [값이 클수록 원의 형태에 가까워짐]
thetaStart?: number, : 시작각도 (radion 단위)
thetaLength?: number : 연장각도
);
*/
// const geometry = new THREE.ConeGeometry(0.3,1, 20, 3, false, 0, Math.PI/2);
/*
# 2. ConeGeometry
constructor(
radius?: number,
height?: number,
radialSegments?: number,
heightSegments?: number,
openEnded?: boolean,
thetaStart?: number,
thetaLength?: number,
)
*/
// const geometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.9, 0.9, 1.6, 30 ,4);
/*
# 3. CylinderGeometry
constructor(
radiusTop?: number,
radiusBottom?: number,
height?: number,
radialSegments?: number,
heightSegments?: number,
openEnded?: boolean,
thetaStart?: number,
thetaLength?: number,
)
*/
// const geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.9, 30, 30, 0, Math.PI * 2);
/*
# 4. SphereGeometry
constructor(
radius?: number,
widthSegments?: number,
heightSegments?: number,
phiStart?: number,
phiLength?: number,
thetaStart?: number,
thetaLength?: number,
)
*/
//const geometry = new THREE.RingGeometry(0.5, 1, 30, 2);
/*
# 5. SphereGeometry
constructor(
innerRadius?: number,
outerRadius?: number,
thetaSegments?: number,
phiSegments?: number,
thetaStart?: number,
thetaLength?: number,
)
*/
// const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(0.5, 1, 30, 2);
/*
# 6. PlaneGeometry
constructor(
width?: number,
height?: number,
widthSegments?: number,
heightSegments?: number
);
*/
// const geometry = new THREE.TorusGeometry(0.9, 0.4, 5, 10, Math.PI *2, 2);
/*
# 7. TorusGeometry
constructor(
radius?: number,
tube?: number,
radialSegments?: number,
tubularSegments?: number,
arc?: number
);
*/
const geometry = new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(0.5, 0.09, 13, 5);
/*
constructor(
radius?: number,
tube?: number,
tubularSegments?: number,
radialSegments?: number,
p?: number,
q?: number,
);
*/
const fillMaterial = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({ color : 0x515151 });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, fillMaterial);
const lineMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color : 0xffff00});
const line = new THREE.LineSegments(
new THREE.WireframeGeometry(geometry),
lineMaterial
);
// 3. 하나의 객체로 만들기 위해 Group으로 묶음.
const group = new THREE.Group();
group.add(cube);
group.add(line);
// Scene에 담음.
this._scene.add(group);
this._cube = group;
}
resize(){
const width = this._divContainer.clientWidth;
const height = this._divContainer.clientHeight;
this._camera.aspect = width / height;
this._camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
this._renderer.setSize(width, height);
}
render(time){
this._renderer.render(this._scene, this._camera);
this.update(time);
requestAnimationFrame(this.render.bind(this));
}
update(time){
time *= 0.001;
}
}
window.onload = function(){
new App();
};주석문에 있는 생성자를 확인하면서 값을 변경해보면 될 것이다.
모든 Geometry객체는 이해가 갔는데,
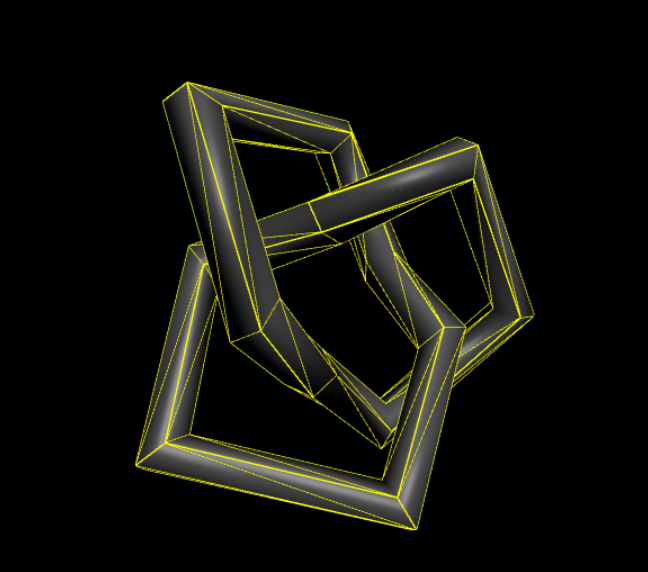
여기서 구현한 Geometry 객체 말고도 많은 객체가 있는데, 공식문서와 생성자를 참고하면서 보면 쉽게 알 수 있을 것이다.
이전 포스팅
[Three.js] Geometry - BoxGeometry와 WireFrameGeometry
Three.js에서 제공하는 기본 Geometry에 대해서 알아보겠다. Geometry는 앞선 포스팅에서 처럼 Mesh에 들어가는 요소 Geometry, Material 중에 형상을 의미하는 거라고 설명했다. 아래 그림은 Three.js 에서 제공
zeroco.tistory.com
[Three.js] Three.js 기본개념
Three.js 에서 가장 기본이 되는 것은 Renderer, Scene, Camera이다. 이 개념을 먼저 익히고 라이브러리의 도식화에 대해서 파악한다. Three.js의 기본개념은, Scene을 만들어 그 안에 3D 객체를 넣고, 그걸 Ca
zeroco.tistory.com
공식문서
three.js docs
threejs.org
'Frontend > Three.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Three.js] 3차원 공간구성 (scene graph) (0) | 2022.07.17 |
|---|---|
| [Three.js] .gltf 파일 로딩하기 (0) | 2022.07.15 |
| [Three.js] Geometry - BoxGeometry와 WireFrameGeometry (0) | 2022.07.13 |
| [Three.js] Three.js 기본개념 (0) | 2022.07.12 |
| [Three.js] 개발환경구성 해보기 (0) | 2022.06.22 |



